

- #Virtual box kitematic how to
- #Virtual box kitematic install
- #Virtual box kitematic software
- #Virtual box kitematic windows
If VirtualBox is already installed on our computer, we must uncheck the checkbox of VirtualBox while running the Docker Toolbox setup and VirtualBox must be closed before the installation. It uses Oracle VirtualBox which is included in the package to run that Linux VM in a virtual environment.
#Virtual box kitematic windows
This VM is going to use to host Docker Engine on our Windows system. So, we need to create and attach a small Linux VM on our host using the Docker Machine command. We cannot run Docker Engine natively on Windows because the Docker Engine daemon uses Linux-specific kernel features to run. Here, we have 3 new Desktop shortcuts as below: Step 9: Click on Finis and it will open a Windows Explorer, close that window and check the Desktop. Here is the final window of the installation as below: Docker Toolbox is installed on our machine.
#Virtual box kitematic install
Step 8: Then, it will install VirtualBox and that’s it. Step 7: If we get the below window, just click on Install: Step 6: It will start the installation and we get progress bar as below: Step 5: Finally, we get the ‘Ready to Install’ window to install the Docker Toolbox, simply click on the Install button: Step 4: Now, we get the window to select additional tasks and we can keep it default and click on next: Now, select the checkboxes as per our requirement and click on the Next button:
#Virtual box kitematic software
I'm a big fan of how easy the Docker team has made it to fire up new database instances (and other software services).Step 3: We get the below window where we have options to select however some checkboxes are greyed-out as those are mandatory ones like if we already have VirtualBox installed on our system then we get the option to uncheck VirtualBox. If you need to change the port, you can do so here: This is the host and port you will use to connect to the database from your application running on localhost.
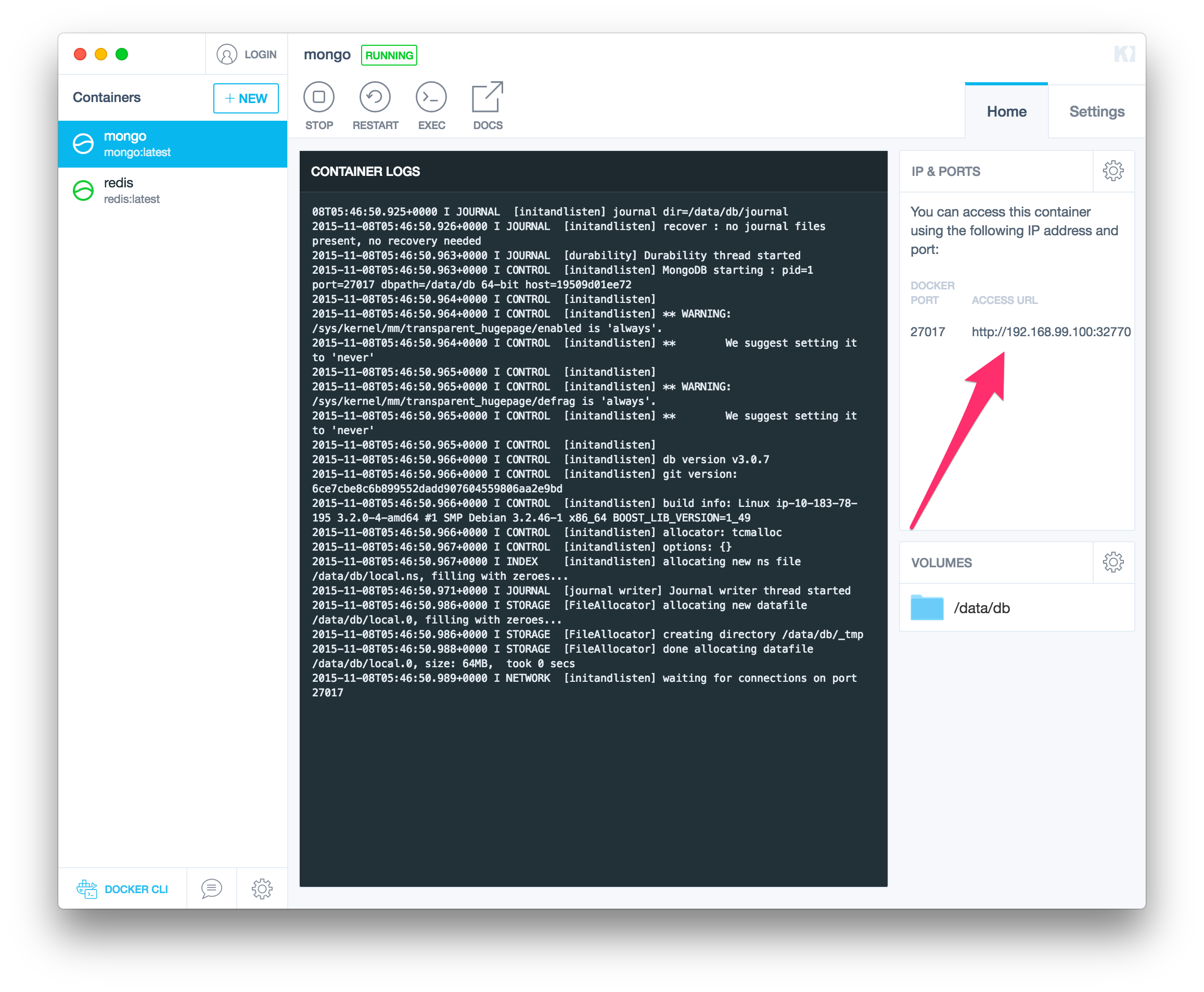
In my case I needed a MongoDB and Redis instance. If you have an account at Docker Hub you can log in here to view your hosted docker repositories, otherwise go ahead and "SKIP FOR NOW" With just one click it will docker pull the image you want, docker run the container instance, and map all of the exposed ports from the automatically generated VirtualBox VM through to your host machine. The extra upside that Kitematic gives you is how easy it is fire up a new container. Kitematic works much the same way: it creates a Virtual Machine inside of VirtualBox, running the lightweight boot2docker OS. If you’ve used Vagrant before, you’re already familiar with these benefits. a different version of MongoDB, Redis, or even WordPress can be installed via Kitematic (and even be running at the same time). This is especially handy if you have different projects that require you to have different versions of the dependency. The great thing about using Docker for local development is that it allows you to install any version of your system-level dependencies or services (referred to as containers) without polluting your host Operating System. Below is a quick walkthrough of one of the most common ways I've been using the new Kitematic GUI: installing databases for local development (in this case MongoDB and Redis). Since Docker released Kitematic as part of Docker Toolbox a few months ago, working with Docker on your local machine has never been easier.
#Virtual box kitematic how to
In an earlier post, we showed you how to set up MongoDB Image Instance with Docker Toolbox using Docker command line tools. Using Kitematic for your local development databases


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
